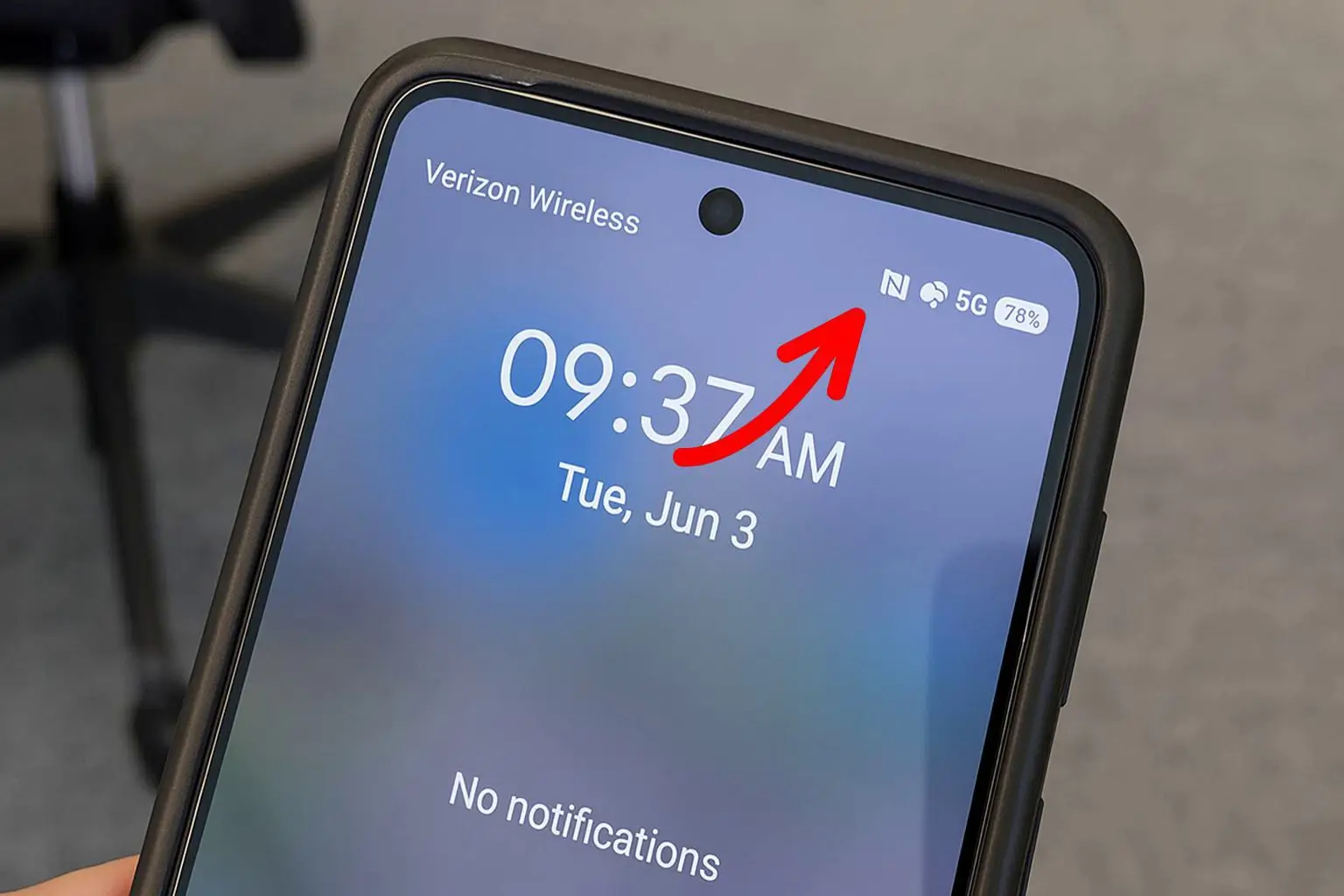
Have you ever noticed a small “N” icon at the top of your smartphone screen and wondered what it meant? For many mobile users, this icon appears without explanation and quickly becomes a mystery. The “N” stands for NFC, which is short for Near Field Communication. It is a short-range wireless technology that enables seamless communication between devices placed close together, typically within 4 centimetres.
In simple terms, the “N” icon tells you that your phone’s NFC feature is enabled. While many users ignore or even turn off this setting, NFC is one of the most powerful and convenient technologies in modern smartphones. From effortless mobile payments to secure device pairing, NFC is transforming how we interact with our devices and the world around us.
What is NFC (Near Field Communication)?
NFC is a contactless communication technology that enables two devices to exchange data when they are close together. Think of it as a more advanced version of RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification). Unlike Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, NFC does not require pairing, passwords, or lengthy setup processes. It is instant, secure, and extremely user-friendly.
Also Read
The “N” icon indicates that your smartphone has NFC switched on, allowing it to scan NFC tags, make payments, share files, or even connect to other devices without complex settings.
How Does NFC Work on Your Smartphone?
NFC operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, meaning one NFC-enabled device can generate a magnetic field that triggers a signal in another. It supports three main modes:
-
Reader/Writer Mode: Your phone reads information from or writes to NFC tags, such as scanning travel passes, product labels, or smart posters.
-
Card Emulation Mode: Your phone imitates a contactless card, letting you use it for payments or building access.
-
Peer-to-Peer Mode: Two NFC-equipped devices exchange data like small files, contact details, or app information.
This instant connectivity is why the NFC feature is increasingly adopted in industries from retail to healthcare.
Why Should You Keep the “N” Icon Turned On?
Many people disable NFC to save battery or out of privacy concerns. However, with smarter phones and improved security measures, leaving NFC enabled is usually beneficial. Here’s why:
Convenience in Payments
The most common use of NFC today is mobile payments through services like Google Pay, Apple Pay, or Samsung Wallet. By tapping your phone on a payment terminal, you can complete transactions in seconds without carrying physical cards.
Enhanced Security
NFC transactions are secured with tokenisation, encryption, and biometric verification. In fact, it is often considered safer than swiping a magnetic stripe card, which is prone to skimming.
Easy Pairing of Gadgets
NFC makes pairing devices (like wireless earbuds, speakers, or printers) instant. Instead of scrolling through menus and entering passcodes, you just tap your phone against the device to establish a connection.
Smart Lifestyle Integration
Smart homes and IoT devices increasingly use NFC tags. With a simple tap, you could turn on lights, adjust thermostats, or even unlock doors configured with NFC-enabled locks.
NFC vs Other Wireless Technologies
NFC is often compared to Bluetooth and QR Codes. While they all serve the purpose of device connectivity or data transfer, their differences make NFC uniquely convenient.
| Feature | NFC | Bluetooth | QR Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Up to 4 cm | Up to 10 metres | Limited by camera & distance |
| Pairing Time | Instant | Several seconds | Manual scanning needed |
| Security | Very High | Moderate | Low (prone to phishing) |
| Power Consumption | Extremely Low | Moderate | None (passive) |
| Main Use | Payments, pairing, access | Audio, file sharing, wearables | Web links, apps, tickets |
This table highlights why the “N” function is often the best choice for secure, fast, and effortless interaction.
Common Everyday Uses of NFC
Modern smartphones have expanded NFC beyond payments. Here are some real-life applications where keeping the “N” icon on proves useful:
-
Public Transport Access: Tap your phone instead of carrying a travel card.
-
Event Tickets: Many concerts and theatres issue NFC-based passes.
-
Contactless Business Cards: Share details with a quick tap.
-
Retail Loyalty Programs: Automate loyalty points collection through NFC-enabled systems.
-
Healthcare Solutions: Hospitals now use NFC tags for patient records and medication verification.
The rise of smart cities and digital wallets means these use cases will only keep growing.
Is NFC Safe to Use?
Yes, NFC is considered highly secure. Since it only works at very close range, it’s hard for hackers to intercept communication. Moreover, most financial transactions require an extra verification step such as Face ID, fingerprint, or PIN.
Battery consumption is also negligible. Unlike Bluetooth that continuously searches for other devices, NFC remains passive until it comes in close contact with another NFC-enabled chip.
Should You Ever Turn Off NFC?
While keeping NFC switched on is safe and convenient, some users may prefer switching it off under specific circumstances:
-
If you rarely use mobile payments or NFC functions.
-
When travelling in regions where NFC is not widely supported.
-
For extended battery saving in low-power situations.
However, for the average smartphone user in the USA, UK, South Africa, or Europe, leaving NFC enabled makes life significantly easier.
The Future of NFC Technology
The “N” icon is becoming essential as society shifts toward a contactless-first world. Retailers, transport authorities, smart homes, and workplaces are adopting NFC at scale. Future possibilities include biometric passports, medical wearables that transmit data instantly, and digital identity verification through NFC wallets.
Major smartphone manufacturers are investing heavily in expanding NFC compatibility, meaning you can expect even more convenience in the coming years.
FAQs
1. What does the little “N” symbol on my phone mean?
It signifies that NFC (Near Field Communication) is enabled, allowing your phone to connect or share data at close range.
2. Is it safe to leave NFC on all the time?
Yes, NFC is secure and consumes minimal power. Most transactions also require biometric verification for added safety.
3. Does NFC drain the battery quickly?
No, NFC uses negligible battery since it stays inactive until near another NFC device or reader.
4. Can I use NFC without internet?
Yes, NFC does not require internet. However, some apps like mobile banking may need connectivity for processing payments.
5. How do I turn on NFC on my phone?
Go to Settings > Connections (or Wireless & Networks) > NFC, then switch it on. The “N” icon will appear in your status bar.